Module 04 Project
Introduction
In this PA you will implement some analysis routines over a data structure called an expression tree. You will implement similar projects in Ruby, Haskell, and Prolog, and the goal is to explore the differences between the three languages.
In Ruby, you will extend existing Ruby classes to practice dynamic object-oriented programming. In Haskell, you will write pattern-matching routines to practice functional programming. In Prolog, you will write rules to practice logical programming.
Project starter files: p4.zip
Requirements
You may ignore Lexer.hs and Parser.hs. They were auto-generated from grammar
specification files using utilities called Alex
and Happy, and they provide the backend code
for parsing simple mathematical expressions. Here is a context-free grammar
(we’ll study these more in-depth in a few weeks!) describing the language that
this parser can recognize:
E -> <int>
| E + E
| E - E
| E * E
| ( E )
You may also ignore the definition of Token in Defs.hs, although you will
need to use the definition of the Expr data type:
data Expr
= EInt Int
| EAdd Expr Expr
| ESub Expr Expr
| EMul Expr Expr
deriving (Show,Eq)
This data type represents nodes in the expression parse tree. For instance, the
expression (2+3)*4 will be parsed into the following tree:
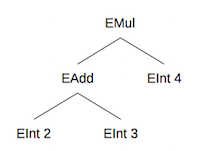
EInt, EAdd, ESub, and EMul are all data value constructors, used to
build or pattern match against an expression tree. EInt represents an integer
terminal node, while the other three represent non-terminal arithmetic operation
nodes. The last line of the Expr definition specifies that we wish to be able
to convert the expressions to strings and compare them using Haskell built-in
recursive definitions.
Using these value constructors, we could represent the parse tree shown above with the following Haskell expression:
EMul (EAdd (EInt 2) (EInt 3)) (EInt 4)
Your task in this PA will be to write various functions to analyze expression trees. You will do this by writing functions that recurse over an expression tree based on data patterns.
You can see an example of a pattern-based function in formatExpr in Defs.hs.
This function takes a tree and matches it against one of the four different
patterns possible using the value constructors, returning a different form of
string for each different pattern.
Most of the functions you write for this PA will have this general form. The function’s input will be an expression tree, and you will specify the output of the function for each pattern that the input could be matched against. You will likely want to make recursive calls in the non-terminal cases.
Below are descriptions of the functions you need to implement. You can also look
at the test cases (in Test.hs) to see what they are supposed to do. You should
think about what the definition of each function means for each Expr pattern.
Unlike in the Ruby implementation, there are no “abstract” classes and so you
will need to write patterns for each value constructor.
eval :: Expr -> Int- Calculates the result of evaluating the mathematical expression. All operations should be done using integer arithmetic.countOps :: Expr -> Int- Counts the total number of arithmetic operations in an expression. All three operations (addition, subtraction, and multiplication) count for this process.height :: Expr -> Int- Calculates the height of the expression tree, where the height of a single-node tree is defined as being 1.postfix :: Expr -> String- Returns a flattened postfix string representation. For example,(2+3)*4in postfix notation would be"2 3 + 4 *". You should use theshowfunction to convert integers to strings.uniqInts :: Expr -> [Int]- Extract a sorted list of all unique integers in an expression. Each integer should appear in the resulting list only once.
For the last function (uniqInts), you may find it helpful to
write two helper functions:
uniq :: Eq t => [t] -> [t]- Returns a copy of the given list with duplicates removed.sort :: Ord t => [t] -> [t]- Returns a sorted copy of the given list.
Some test routines are included in Test.hs. However, your submission will be
graded based on additional tests not provided to you, so you should write your
own test cases as well. You can also test your routines via the provided REPL
(read/eval/print loop) by running Main.hs.
For this assignment, you may NOT use any classes or methods that are not in the Haskell Prelude. If you are unsure about a particular class or method, you can consult the documentation.
Submission
Your program must contain implementations as described above. You must name your
Haskell script file P4.hs. You must put your name in a comment at the top of
the file. As usual, decompose your methods to make them more readable, use good
names, indent properly, and so on. You will partly be graded on the readability
of your code but mostly on whether it works.
Submit ONLY P4.hs to the appropriate assignment on Canvas by the deadline.