Module 04 Project
Introduction
In this PA you will implement some analysis routines over a data structure called an expression tree. You will implement similar projects in Ruby, Haskell, and Prolog, and the goal is to explore the differences between the three languages.
In Ruby, you will extend existing Ruby classes to practice dynamic object-oriented programming. In Haskell, you will write pattern-matching routines to practice functional programming. In Prolog, you will write rules to practice logical programming.
Project starter files: p2.zip
Requirements
You may ignore lexer.rb and parser.rb. They were auto-generated from grammar
specification files using utilities called
Rexical and
Racc, and
they provide the backend code for parsing simple mathematical expressions. Here
is a context-free grammar describing the language that this parser can recognize:
E -> <int>
| E + E
| E - E
| E * E
| ( E )
You will want to take a look at the definitions in defs.rb, which defines the
following class hierarchy:
- Expr
- EInt
- EBinOp
- EAdd
- ESub
- EMul
These classes represent nodes in the expression parse tree. Expr and EBinOp
are parent classes that for the purposes of this project should be considered
abstract. EInt represents an integer leaf node, while the other three
represent interior arithmetic operation nodes. For instance, the expression
(2+3)*4 will be parsed into the following tree:
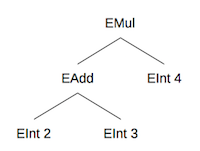
Your task in this PA will be to extend the provided expression tree node classes to analyze expression trees. Because class definitions in Ruby are dynamic, you can add new members to a class definition at any point by providing another class definition with the new members.
For example, when placed in p2.rb, the following code will add a new min_int
function to all concrete expression node classes (recall that any subclasses
that do not override a method will inherit the parent class’s implementation):
class EBinOp
def min_int
[left.min_int, right.min_int].min
end
end
class EInt
def min_int
@val
end
end
Below are descriptions of the methods you need to add. You can also look at the test cases to see what they are supposed to do. You should think about what the definition of each function means for each expression tree node type, and you certainly do not need to implement every method in every class.
eval- Calculates the result of evaluating the mathematical expression. All operations should be done using integer arithmetic.count_ops- Counts the total number of arithmetic operations in an expression. All three operations (addition, subtraction, and multiplication) count for this process.height- Calculates the height of the expression tree, where the height of a single-node tree is defined as being 1.postfix- Returns a flattened postfix string representation. For example,(2+3)*4in postfix notation would be"2 3 + 4 *". You should use theto_smethod to convert integers to strings.uniq_ints- Extract a sorted list of all unique integers in an expression. Each integer should appear in the resulting list only once.
Some test routines are included in test.rb. However, your submission will be
graded based on additional tests not provided to you, so you should write your
own test cases as well. You can also test your routines via the provided REPL
(read/eval/print loop) by running main.rb.
For this assignment, you may NOT use any classes or methods that are not in the
Ruby Core (i.e., you shouldn’t require anything). If you are unsure about a
particular class or method, you can consult the
documentation. Also, we will test your
submission using Ruby 2.6 so you shouldn’t depend on any features added after
that version.
Submission
Your program must contain implementations as described above. You must name
your Ruby script file p2.rb. You must put your name in a comment at the top of
the file. As usual, decompose your methods to make them more readable, use good
names, indent properly (indentation is conventionally two spaces in Ruby), and
so on. You will partly be graded on the readability of your code but mostly on
whether it works.
Submit ONLY p2.rb to the appropriate assignment on Canvas by the deadline.